Objectives
To assess the outcome of different intervention (lifestyle, metformin and glibenclamide) models to prevent diabetes among high risk group in Bangladesh.
Background
Body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio have been shown to be associated with type 2 diabetes. But this association was found to be highly ethnically sensitive. In most epidemiological studies high waist-to-hip ration (WHR) or central obesity has been found significantly related to insulin resistance which in turn related to diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia like high triglycerides (TG), high total cholesterol (T-cho) and low high density-lipoprotein-c (HDL-C). Never the less, all these information were derived from cross-sectional data. Previous reports showed that Asian Indian and Bangladeshi subjects were more sensitive to central adiposity for the development of diabetes.
Most of the data are based on cross-sectional studies and therefore are not liable to identify risks in Asian subjects for diabetes. Therefore the proposed study will be a follow-up study including 5,000 populations to estimate the occurrence of new cases (incidence) of diabetes based on five and ten years follow-up. The biophysical (blood pressure and anthropometrical, height, weight, BMI, waist and hip circumference) and biochemical (T-cho, TG, HDL-cho) risks will be measured. In addition to these known risk factors, their family history of diabetes, physical activity level related occupation, and food habits would be assessed as a lifestyle factor.
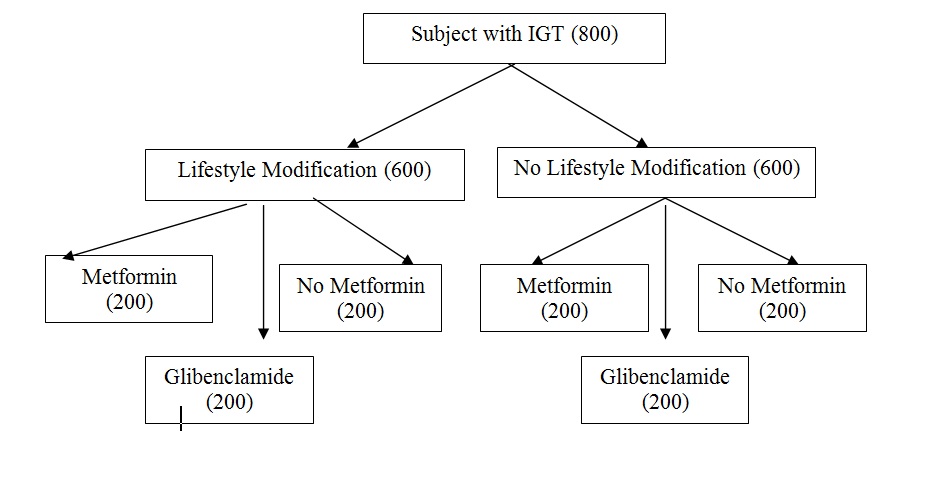
Onethousand and five hundred with Impaired Glucose Tolerance were recruited for intervention and followed for 18 months. Those willing to participate will then be stratified randomly by Age and BMI (Normal and Overweight/Obese) into four different arms. The study will be prospective intervention trail to assess the impact of different intervention modules to find out appropriate prevent the diabetes among high risk groups.
Figure of the Study Design
Financing
Cooperation
- Bangladesh Institute of health sciences
- Diabetes association of Bangladesh
Start - Finish
2009 - 2012
